Why do I need to perform a qPCR? Can this step be skipped?
Performing a qPCR assay is recommended to determine the Optimal Endpoint PCR cycle number (OEP). This prevents under- or over-cycling, which may have negative effects on downstream applications. Undercycling results in low yields and often insufficient material for downstream use, while overcycling will result in a loss of longer full-length cDNAs (see Figure). Once the number of cycles for the endpoint PCR is established for a particular RNA sample type (including RNA quality level) and input amount, the same can be used for the following experiments without performing the qPCR each time. See also Appendix B of the TeloPrime V2 User Guide.
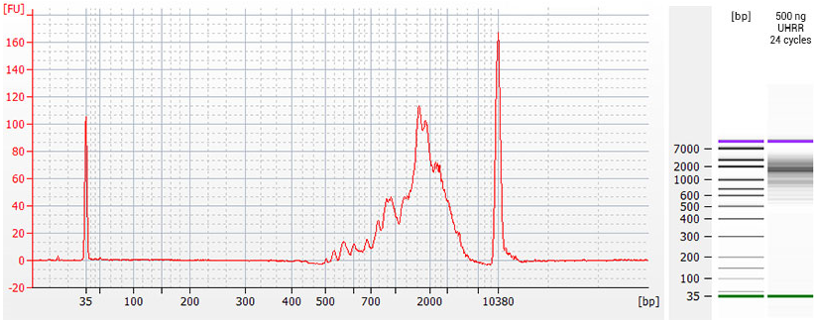
Figure | TeloPrime cDNA Quality Control. TeloPrime cDNA was prepared from 500 ng of Universal Human Reference RNA (UHRR). Amplification was performed using 1 µl of cDNA with 24 cycles of PCR. Final cDNA was run at 1:10 dilution on a Bioanalyzer High Sensitivity DNA Chip (Agilent Technologies). The optimal endpoint PCR (OEP) cycle number was determined by qPCR as described in Appendix B, p.22.
The TeloPrime Full-Length cDNA Amplification V2 Kits (Cat. No. 013) contain sufficient reagents to perform a qPCR and endpoint PCR for each sample. Lexogen also offers a TeloPrime PCR Add-on V2 Kit (Cat. No. 018) for 16 reactions if additional PCRs are required.
